
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
With the continuous improvement of people's requirements for safety and comfort during car driving, automotive radars are widely used in automotive adaptive cruise systems, anti-collision systems, and driving support systems. Among them, millimeter-wave radar is widely used because of its high detection accuracy, small hardware size, and immunity from severe weather.
However, the traditional single radar sensor still has shortcomings such as small detection range and low reliability. Especially in complex driving conditions, merging, shifting, turning, up and down, and static guardrails, signs, and pedestrians on both sides of the road will make it very difficult for the radar to identify the main target, and the false alarm rate is high.
To completely solve the problem of radar false alarms, it is also necessary to adopt information fusion technology between multiple sensors. A network system formed by integrating various radar sensors together integrates the advantages of various sensors, realizes information analysis, synthesis and balance, and uses the redundancy and complementary characteristics of data for fault-tolerant processing, which overcomes the reliability of a single sensor The shortcomings of low performance and small effective detection range effectively reduce the false alarm rate of radar. The new, high-precision sensor network formed by this can greatly improve the performance of the automotive radar network system.
The composition principle of the radar network
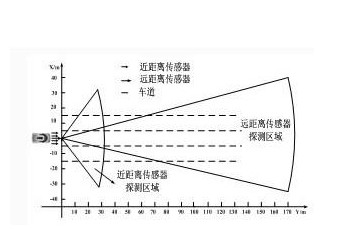
The radar network shown in Figure 1 consists of four short-range millimeter-wave radar sensors equidistantly distributed on the safety bar
(Neardistancesensor, NDS) structure, each radar sensor adopts FMCW system. The sensor network can achieve a horizontal azimuth of 120° coverage within a range of 35 meters. This kind of short-distance, large-coverage radar sensor network can monitor the vehicle's forward target in a larger range when the vehicle speed is not high and the road conditions are more complicated (such as urban traffic).
If long-distance detection is required, a long-distance radar sensor can be added in the middle of the safety bar. With the maturity of 77GHz automotive radar sensor technology, near/long-distance radar sensors tend to adopt 77GHz MMIC (millimeter wave integrated circuit) technology. It is easy to make integrated design schemes using this technology, and the cost of transceiver modules is greatly increased. reduce.
In the sensor network system block diagram shown in Figure 2, the radar sensor based on 77GHzMMIC technology is the front-end key hardware that constitutes the automotive radar network, and the back-end information processing needs to be completed by high-speed computing units such as digital signal processors. Sensors, digital signal processing units, and data fusion decision-making systems use Ethernet and high-speed serial connections to transmit data to meet high data rate transmission requirements.
The data fusion system adopts a distributed architecture, that is, each short-range sensor first performs local processing on the echo signal obtained, and then sends it to the fusion center for fusion to obtain the target's position and speed information. The controller is the final decision-making body of the entire radar network system. It is responsible for identifying whether the distance and speed information of the target poses a threat to driving safety, and prompts the driver through sound and light or directly acts on the on-board control system to adjust.

Figure 2 Radar network system structure diagram
Key technology solutions for automotive radar networks
Compared with a single radar sensor, the advantages of multi-sensor networking are high measurement accuracy, low false alarm rate and superior performance of multi-target recognition. The high measurement accuracy and low false alarm rate are due to data fusion technology, which requires each sensor to be accurately synchronized in time and frequency; multi-target recognition depends on the system's own ability to recognize and classify targets. Therefore, the design of the entire radar network, including each radar sensor, must focus on these two points.
1 Proximity sensor design
The short-range radar sensor is mainly responsible for the detection of targets within 35 meters of the car's forward direction, and is a key part of the car's radar network to exert its effectiveness in complex road conditions. The close range radar sensor mainly includes the precise time synchronization control between the radio frequency unit, the receiver and each sensor. In the design of the antenna, it is necessary to meet the requirements of the beam width shown, and at the same time, the volume of the sensor cannot be increased. Therefore, a printed linear array antenna can be used.
The receiver is mainly composed of some low-frequency components, anti-aliasing filters and analog-to-digital conversion devices. The noise generated by these low-frequency components can submerge the weak echo signal, which is one of the main factors affecting the detection distance, so the noise parameters should be reduced as much as possible. In addition, the sampling frequency of analog-to-digital conversion should be determined based on the performance parameters of the proximity sensor. The schematic diagram of the proximity sensor is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3 Close-range sensor structure diagram
2 Synchronous control
After the radar is networked, the position of the target is also determined by measuring the frequency difference between the transmitted signal and the echo signal. But different from single radar detection, the distance and speed of the target measured by the automotive radar network are obtained by data fusion of the target information measured by each sensor. In order to measure the target distance and generate a consistent waveform, the transmitter and receiver must have a unified time standard, which is synchronization in time.
In order to receive and amplify the echo signal, the transmitter and receiver of the radar sensor must work at the same frequency. When the transmitter frequency is agile, the receiver local oscillator must change accordingly, that is, to achieve frequency synchronization. The automotive radar network requires the time synchronization control error between the sensors to be within 10ns. Therefore, the high-precision time-frequency synchronization system is the key technology of automotive radar sensor networking.

Figure 4 Block diagram of the synchronization system
Figure 4 shows the configuration based on the DDS synchronous clock source. The reference frequency source of the DDS synchronous clock source on each transceiver unit should be a high-stability atomic clock (such as rubidium, cesium atomic clock). The atomic clock of each transceiver unit should be calibrated with the same time reference regularly. The accuracy of the time reference used for calibration is higher. They can be GPS (Navigator Global Positioning System), Roland C or the time reference signal transmitted by the color TV transmitter.
3 Target classification algorithm of automotive radar network
The main task of the target classification system is to calculate the classification relationship of a given vector according to the characteristics of the target echo signal. The classifier defines a set of different target categories. The work of the classifier can be divided into a research phase and a classification phase. In the research phase, the classifier automatically analyzes several features and independently labeled feature vectors; in the classification phase, a feature vector is generated for each detected target.
At the same time, the recognition algorithm uses the maximum likelihood method to make a decision to determine which class the feature vector belongs to, as shown in Figure 5. In automotive applications, due to the complexity of the classification task, usually a given vector needs to consider several features, so multiple classifiers are used. The advantage is that a certain feature can be evaluated in an iterative process during the research phase. And automatically eliminate items that have less impact on the decision-making process.
Based on the system structure and signal processing process of the target classification system of automotive radar sensors, it can identify six different radar target categories, including: pedestrians, cyclists, vehicles, crowds, trees, and traffic signs.
4 Moving target position estimation algorithm

Figure 5 The classification and processing process of the vehicle radar to the target
The basic principle of FMCW radar is to use the frequency difference between the transmitted and echo signals to determine the distance and speed of the target [5]. The traditional FMCW adopts equal-period frequency modulation, which is simple and feasible in the case of measuring a single target, and shows good real-time performance and range and speed measurement functions. But when there are multiple targets in the front, the radar will have difficulty in judging. In order to identify the distance and speed of multiple targets, the FMCW waveform with variable period can be used as the transmission signal. Literature [6] gives an algorithm for measuring the distance and speed of a target using a variable-period transmission signal.

Figure 6: Car radar network achieves measurement of single target
For the radar network system discussed in this article, the four short-range radar sensors are both transmitters and receivers. As shown in Figure 6, through the control of the electric scan switch, one of the NDSs acts as a transmitter, and the reflected signal is received by the four NDSs at the same time. After signal processing, due to the different positions of each NDS, four groups of distance and relative speed values (r1, 1v1, 1), (r1, 2v1, 2), (r1, 3v1, 3) about the measured target can be obtained. ), (r1, 4v1, 4). This kind of radar network system that adopts single-station transmission and multi-station reception, although it requires high time synchronization control between sensors, it can avoid mutual interference between neighboring sensors.
The distance and speed of the target measured by the automotive radar network are obtained by data fusion of the target information measured by each sensor. In a measurement period, each NDS takes turns to act as a transmitter. Therefore, there are 16 combinations of distance and relative speed, expressed as a vector:
In the Cartesian coordinate system, the target's state vector is used to express the target's position vector and relative velocity vector:

The position of each sensor in the Cartesian coordinate system is represented by a vector as:

For each sensor, if the position of the sensor and the target in the coordinate system is known, the distance can be calculated by the following nonlinear equation:

In the same way, the equation about the relative speed of the target is obtained:

(5) Combining equations (1), (2), (4), (5), we can obtain multiple nonlinear equations of the state vector of the target and the distance and velocity of the target measured by the four sensors, expressed as a vector function :

The derivative matrix, which is the Jacobian matrix, is:

(7) Using Gauss-Newton iterative algorithm for equation (7) can accurately calculate the parameter value of the target state vector, and then the target position and relative velocity value can be obtained. Because the above calculation can give the Cartesian coordinates of the moving target position, it is very convenient to determine the accuracy and resolution of the position estimation [7].
Development status of millimeter wave automotive radar network
At present, although the 77GHz frequency band of the millimeter wave automotive radar network has been fully studied in the world, there are differences in each country as to the specific frequency band. One of the focus of the current debate on the short-range radar sensor for automobiles is the use of the 24GHz frequency band. Still the 77GHz frequency band. The reason for the controversy is the cost and technological maturity of 77GHz radar devices. Therefore, the cost and technological maturity of 77GHz radar sensors are the key to whether the automotive radar network can be widely used in the market.
In the research and development of 77GHz radar sensors, the key technology is how to use GaAs (gallium arsenide) device technology to design and manufacture low-cost automotive near/long range radar sensors, thereby reducing the cost of the entire automotive radar network. The foreign GaAs device manufacturing industry has developed rapidly, and some highly cost-effective automotive radar sensors have appeared. Some reports even predict that the market for automotive radar networks will start at the end of 2007 and 2008, and it is expected to become the basic configuration of popular cars. .
Compared with other systems, automotive radar networks have a much lower technical threshold. At present, the development of China's automotive radar is mainly focused on the level of car reversing radar and car radar speed measuring device. The technologies and frequency bands used are very different. Distance radar sensors, moving target position estimation algorithms, moving target classification, automotive signal processors and other multi-level, system and industrial chain perspectives to research and develop automotive radar network technology, which is in line with the increasingly popular research and development of automotive radar in the world. Compared with the application, there is still a big contrast. This situation is incompatible with China's status as a global automobile consumer.
Author:
Mr. yin chang
March 14, 2025
March 07, 2025
Why you could choose our brake disc manufacture?First one and foremost, your would get brake discs which made of high quality materialSecond, you would gain brake discs competitive and reasonable...
Model NO.: DF-ST45 Model NO.: DF-ST45 ITEM: STARTER MOTOROur company has reached over 10 years manufacturing experience in the Automobile production market and has exploited around 150 kinds of...
The role of three-terminal regulator It is generally used in the protection circuit of DC circuit to reduce the voltage and stabilize the voltage. +The commonly used 78 series and 79 series, 78XX are...
The wax thermostat has stable operation, low water flow resistance, large flow into the radiator, firm structure, long service life, heat resistance, freeze resistance and pressure resistance. Due to...
Email to this supplier
Author:
Mr. yin chang
March 14, 2025
March 07, 2025
Copyright © 2026 YIWU JINGHONG AUTO PARTS CO.,LTD All rights reserved. Privacy Policy

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.